Category: Information Systems
Empowering Developers for Seamless Collaboration – GitHub Tools
GitHub has emerged as a pivotal platform in the world of software development, providing a robust ecosystem for version control and collaboration. In this article, we delve into the intricate details of GitHub repository hosting, elucidating how developers can create, host, and manage Git repositories effortlessly while emphasizing the collaborative tools that GitHub offers.
Creating and Hosting Git Repositories:
GitHub simplifies the process of creating and hosting Git repositories, making it accessible for developers of all skill levels. To start, developers can initiate a new repository directly on the GitHub website or utilize the Git command line to push an existing repository. This process involves defining repository details such as name, description, and visibility (public or private).
Once a repository is created, developers can use Git commands to commit changes and push them to the GitHub repository. This integration ensures that the entire team can access the latest codebase, fostering a collaborative and efficient development environment. GitHub’s reliability and scalability make it an ideal choice for hosting repositories, ensuring seamless code collaboration.
Management Tools on GitHub:
GitHub goes beyond being a simple hosting platform; it offers a suite of tools for effective project management. These tools enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and contribute to the overall efficiency of development teams.
- Issue Tracking: GitHub’s issue tracking system allows developers to report and manage bugs, feature requests, and other tasks effectively. Issues serve as a central hub for communication, providing a structured way for team members to discuss, assign, and prioritize work. Developers can create issues, comment on them, and link them to specific branches or pull requests, creating a comprehensive overview of project tasks.
- Code Review: GitHub’s pull request (PR) feature facilitates code review, a crucial aspect of collaborative development. Developers can submit a branch as a pull request, enabling team members to review the code changes, leave comments, and suggest improvements. The visual representation of code changes and discussions within the PR interface streamlines the review process, ensuring that the team maintains code quality and consistency.
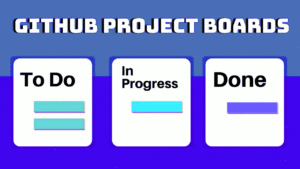
- Project Management: GitHub provides project boards to organize and manage tasks in a visually intuitive way. These boards can be customized to align with the team’s workflow, incorporating columns for to-do, in-progress, and completed tasks. This flexibility empowers teams to adapt GitHub to their specific project management methodologies, be it Agile, Scrum, or Kanban.
Collaboration Advantages:
GitHub’s collaboration features foster a culture of teamwork and transparency among developers. By centralizing communication, tracking issues, and streamlining code reviews, GitHub ensures that the entire team remains on the same page throughout the development lifecycle. Moreover, the platform’s accessibility encourages open-source collaboration, enabling developers worldwide to contribute to diverse projects.
GitHub has evolved into a powerhouse for software development, offering not only reliable repository hosting but also a rich set of tools for collaboration and project management. Developers can create, host, and manage Git repositories effortlessly, while GitHub’s collaborative features enhance communication and streamline workflows.
As the software development landscape continues to evolve, GitHub remains a cornerstone in the quest for efficient, collaborative, and high-quality code development.
GIT Basics
What is Git?
Git is a distributed version control system (DVCS) that helps developers manage and track changes in their source code during software development. It allows multiple people to collaborate on a project simultaneously while keeping a complete history of all changes made to the codebase. Git is known for its speed, data integrity, and flexibility.
Creator of Git
Git was created by Linus Torvalds, the same individual who created the Linux operating system.
Importance of Git
Git is crucial in software development for several reasons:
- Version Control: Git tracks changes to code, enabling developers to work on different features or bug fixes in parallel without conflicts. This version control system ensures code integrity.
- Collaboration: Git facilitates collaboration among developers by allowing them to merge their changes seamlessly, even if they’re working remotely. This is vital for open-source projects and distributed teams.
- History and Documentation: Git maintains a detailed history of code changes, which acts as documentation. Developers can review the history to understand when, why, and how changes were made.
- Branching: Git’s branching system enables the creation of separate lines of development. This is useful for developing new features, experimenting, and isolating bug fixes.
- Reverting Changes: Developers can easily revert to a previous state if a bug is introduced or if a new feature doesn’t work as expected.
- Backup: Git repositories act as backups, ensuring that code is not lost, even if a local machine fails.
Evolution of Git
- Git was first released by Linus Torvalds in 2005.
- It gained popularity quickly due to its efficiency and distributed nature.
- GitHub, a web-based platform for hosting Git repositories, was launched in 2008. It played a significant role in popularizing Git by providing a user-friendly interface and collaboration tools.
- Git has evolved over the years with numerous updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
- Git has become the de facto version control system in the software development industry, used by millions of developers and organizations worldwide.
GitHub
GitHub is a web-based platform built on top of Git, designed to make collaborative software development easier. It provides:
- Repository Hosting: Developers can create, host, and manage Git repositories on GitHub.
- Collaboration: GitHub offers tools for issue tracking, code review, and project management, making it easier for teams to work together.
- Social Features: Developers can follow others, star repositories, and contribute to open-source projects hosted on GitHub.
- Continuous Integration: GitHub Actions allows for automated testing and deployment directly from repositories.
- Integration: It integrates with various third-party tools and services, enhancing the development workflow.
GitHub has become a central hub for open-source projects and a valuable resource for developers and organizations to share, collaborate on, and distribute their code.
In summary, Git is a version control system that helps developers manage code changes efficiently, and GitHub is a web-based platform that enhances the collaborative aspect of Git, making it easier for developers to work together on projects. Both Git and GitHub have had a profound impact on the world of software development.
Linux Powers Web Evolution
In today’s digital age, we rely heavily on websites for various purposes, from shopping and communication to accessing information and entertainment. These websites are hosted on servers that handle the vast amount of internet traffic generated every day. Linux servers, with their robustness, scalability, and security, have emerged as a dominant force in supporting a majority of the internet traffic.
Linux, an open-source operating system, has become the preferred choice for web hosting due to its stability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Its ability to efficiently manage high volumes of requests, handle concurrent connections, and optimize resource utilization makes it an ideal platform for hosting websites. Linux also provides a wide range of server software, such as Apache and Nginx, which are well-known for their performance and reliability.
The evolution of web development in Linux systems has witnessed significant advancements. Initially, web development relied on Common Gateway Interface (CGI) technology, which allowed web servers to execute scripts to generate dynamic content. In the early days, scripting languages like PERL were commonly used in Linux environments for CGI programming.
Later on, the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP/Python/Perl) gained prominence as a powerful and popular web development environment. Linux served as the operating system, Apache as the web server, MySQL as the database management system, and PHP/Python/Perl as the scripting language. LAMP provided a comprehensive solution for developing dynamic websites and web applications, and it became the foundation for many successful web projects.
As technology progressed, new concepts and tools emerged in the web development landscape, including serverless architecture and frameworks like Node.js. Serverless computing abstracts away the infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus solely on writing code. It enables automatic scaling, reduced costs, and simplifies the deployment process. While Linux servers continue to play a crucial role in hosting serverless applications, the architecture itself provides a more efficient and scalable approach to building web services.
Node.js, a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine, has gained immense popularity for developing server-side applications. With Node.js, developers can use JavaScript on both the client and server sides, enabling a unified and streamlined development process. Its non-blocking and event-driven architecture make it highly efficient, especially for handling concurrent connections and real-time applications.
The integration of Node.js with Linux systems has further expanded the possibilities in web development. Linux’s compatibility with Node.js allows developers to leverage its powerful features, such as the vast collection of open-source modules available through the Node Package Manager (npm). This combination has facilitated the creation of scalable, high-performance web applications and APIs.
As a matter of fact, Linux servers have emerged as the backbone of the internet, supporting the majority of web traffic. The evolution of web development in Linux systems has witnessed the transition from CGI and PERL to the LAMP stack and, more recently, the emergence of serverless architecture and tools like Node.js. As technology continues to evolve, Linux remains a reliable and versatile platform for hosting websites, while new concepts and tools provide developers with more efficient and innovative ways to build web applications.
Empowering e-Governance in India: How the National Informatics Centre (NIC) Supports the Development of Government Websites, Including Health Programs
The National Informatics Centre (NIC) is a premier information technology organization of the Indian Government that provides e-governance solutions and support to various government departments and agencies. The organization was established in 1976 and has since played a crucial role in the development and implementation of various government programs and initiatives.
NIC supports the development of government websites, including those related to health programs, by providing technical expertise, infrastructure, and software applications. NIC provides various services such as website design, web hosting, content management system (CMS) development, and data center services to government departments and agencies.
NIC also provides support for the implementation of e-governance initiatives such as the National Health Stack, which aims to create a shared digital infrastructure for healthcare service delivery across the country. The National Health Stack includes various components such as the National Health ID, Health Data Management Policy, Federated Personal Health Records (PHR) system, and Health Analytics Platform, which aim to create a comprehensive health information system that can be used to improve healthcare service delivery and outcomes.
In summary, the National Informatics Centre plays a crucial role in supporting the development and implementation of government websites, including those related to health programs, by providing technical expertise and infrastructure support. The organization’s contribution is critical to the success of various e-governance initiatives, including the National Health Stack, which aims to improve the delivery of healthcare services in India.
Important concepts for setting up websites.
Setting up a website can be an exciting and rewarding process, but it can also be daunting if you’re new to it. Here are 5 basic concepts to keep in mind when setting up a website:
- Domain Name: A domain name is the address of your website on the internet. It’s the name that people will type into their web browser to find your site. Choosing the right domain name is important as it can affect your website’s branding, search engine optimization, and overall success. Make sure the domain name you choose is relevant to your website’s content and easy to remember.
- Web Hosting: Web hosting is a service that allows you to store your website’s files and data on a server that’s accessible on the internet. When choosing a web hosting provider, consider factors such as reliability, uptime, security, and customer support. It’s important to choose a web hosting plan that meets your website’s needs and budget.
- Content Management System (CMS): A content management system is a software application that allows you to create, manage, and publish digital content. Popular CMS platforms include WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla. When choosing a CMS, consider factors such as ease of use, scalability, and community support.
- Website Design: The design of your website is important as it can affect user experience, engagement, and conversion rates. When designing your website, consider factors such as layout, typography, color scheme, and branding. Make sure your website is visually appealing, easy to navigate, and optimized for different devices and screen sizes.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): SEO is the process of optimizing your website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves optimizing your website’s content, structure, and technical aspects to improve its visibility and relevance to search engines. When setting up your website, make sure to implement basic SEO practices such as keyword research, on-page optimization, and link building.
These are just a few basic concepts to keep in mind when setting up a website. As you delve deeper into the process, you’ll encounter more advanced concepts such as website analytics, e-commerce integration, and web security. However, understanding these basic concepts can help you lay a solid foundation for your website’s success.
When setting up an advance website, there are several important concepts to keep in mind, including the basic ones and the concept of dynamic website. For dynamic websites like Social Networking, Online Flight Ticket Booking etc., you’ll need to consider web development frameworks and must also know about the databases.
Web Development Frameworks: Web development frameworks provide a set of tools, libraries, and pre-built components that make it easier to develop dynamic websites. Popular web development frameworks include PHP (Laravel, CodeIgniter), Java (Spring, Hibernate), and Python (Django, Flask). When choosing a web development framework, consider factors such as ease of use, scalability, and community support.
Databases: Databases are used to store and manage website data such as user information, product catalogs, and website content. Popular databases for web development include MySQL, Oracle, and MongoDB. When choosing a database, consider factors such as data structure, scalability, and performance.
PHP is a popular server-side scripting language that is commonly used for web development. It has a large community of developers and a wide range of web development frameworks such as Laravel and CodeIgniter. MySQL is a popular database choice for PHP developers.
Java is another popular server-side programming language that is often used for enterprise web development. It has a wide range of web development frameworks such as Spring and Hibernate. Oracle is a popular database choice for Java developers.
Python is a versatile programming language that is often used for web development. It has a wide range of web development frameworks such as Django and Flask. MongoDB is a popular database choice for Python developers.
In summary, when setting up a website, it’s important to consider the basics such as domain name, web hosting, CMS, website design, and SEO. If you’re looking to build a dynamic website, you’ll need to consider web development frameworks, scripting languages and databases. By choosing the right tools and technologies, you can build a successful website that meets your needs and those of your users.
How Information Systems Support Public Health Programs in India
Information systems (IS) are systems that use information and communication technologies (ICT) to capture, store, manage, process, and distribute data and information for various purposes within an organization or across organizations. Information systems play a critical role in supporting the operations, decision-making, and strategic planning of businesses and other types of organizations. The main components of an Information System are – Hardware, Software, Data, Procedures & People.
Hardware: In the context of national public health programs in India, hardware refers to the physical devices used to store and manage data at various levels of the healthcare system. This includes servers, data centers, and computer systems used by government agencies, healthcare facilities, and other stakeholders to capture, store, and process health data related to public health programs.
Software: Software plays a crucial role in national public health programs in India, as it includes applications and systems used for data management, reporting, and analysis. This may include disease surveillance systems, electronic health record (EHR) systems, data analytics tools, and reporting platforms used by government agencies to monitor the progress and effectiveness of public health programs.
Data: Data is a critical component of national public health programs in India, as it includes information related to disease prevalence, population health indicators, and program outcomes. This data is collected, stored, and analyzed in information systems to inform policy decisions, program planning, and resource allocation.
Networks: Networks are essential for the exchange of data and information in national public health programs in India. This may include networks that connect different levels of the healthcare system, such as district, state, and national levels, to facilitate data sharing, reporting, and communication among various stakeholders involved in public health programs.
Procedures: Procedures are vital in national public health programs in India to ensure data accuracy, quality, and security. This may include protocols for data collection, data validation, and data entry, as well as standard operating procedures for reporting, data sharing, and data privacy in compliance with relevant regulations and guidelines.
People: People play a crucial role in national public health programs in India, as they are the users, managers, and beneficiaries of information systems. This includes healthcare professionals, government officials, public health workers, and other stakeholders who use information systems to collect, manage, and analyze data to inform decision-making, program planning, and implementation.
In the context of national public health programs in India, information systems encompass hardware, software, data, networks, procedures, and people, which collectively support data-driven decision-making, program management, and monitoring to improve the effectiveness and impact of public health programs in the country.